Tempered Glass
Last Updated: July 30, 2024
Share Article
Tempered Glass
Tempered Glass
Tempered glass is a type of safety glass that has been thermally treated to significantly increase its strength compared to standard annealed glass. This process involves heating the glass to a high temperature and then rapidly cooling it to induce surface compression. As a result, tempered glass is at least four times stronger than annealed glass of the same thickness in resisting windload.
In the event of breakage, tempered glass shatters into very small particles, reducing the risk of serious injury. However, because these small fragments may evacuate the opening, they can pose a risk of damage or injury to people below. Therefore, tempered glass should be used judiciously in commercial construction.
Tempered glass meets the ASTM C1048 specification, which requires that 6mm glass have a minimum surface compression of 10,000 psi (69 MPa). Additionally, tempered glass complies with ANSI Z97.1 and CPSC 16 CFR 1201 safety standards. ANSI Z97.1 sets safety requirements for glazing materials used in buildings, including impact and center punch fragmentation testing. CPSC 16 CFR 1201 is a Consumer Product Safety Commission standard that specifies the safety performance requirements for architectural glazing materials. These standards ensure that tempered glass provides the necessary safety and performance for use in doors, windows, and other critical applications where safety glazing is essential.
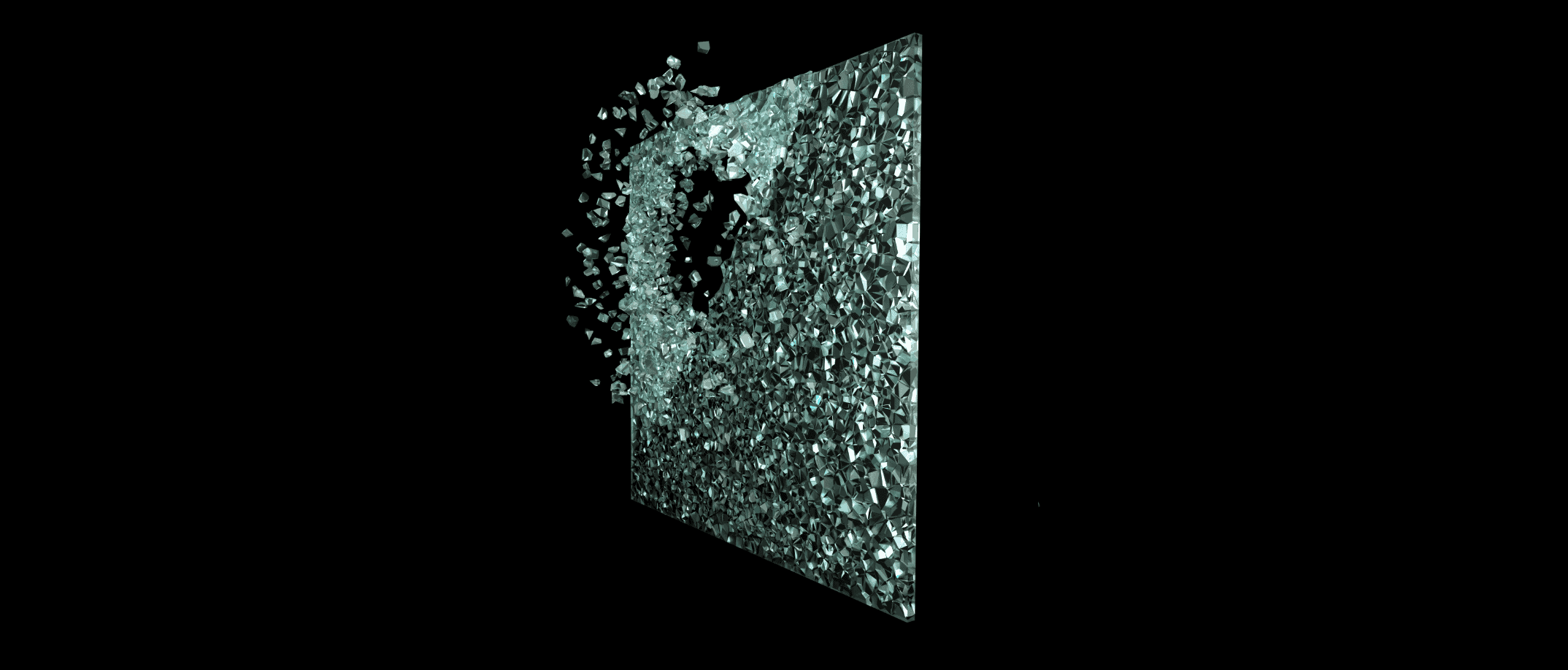
Figure: Tempered glass break pattern
Cardinal advises the use of tempered glass primarily for specific applications where safety glazing codes are mandated. Such applications include door assemblies, sidelights, and certain window varieties. Since tempered glass possesses a strength approximately four times greater against windload, it is an ideal choice for large windows. Additionally, it is apt for fire knockout panels, wherein the glass serves as a protective barrier but can be readily shattered to allow emergency access. In situations where there’s minimal risk of glass fallout, tempered glass may also be deemed suitable.
More:
Related Glossary Entries:
Other Resources:
CONTINUE READING


